Our design process according to the principles of APQP
In the competitive world of manufacturing, quality isn’t a luxury – it’s a necessity. Quality failures can ruin a business’ reputation quickly. That makes the introduction of new products – or any significant changes to existing ones – a particularly delicate process.
Risk management and the continuous optimization of our quality standards are important parts of the way we work. This is reflected in every step of our development process. Interested in how we develop custom plastic extrusion parts at Meldon? In this blog, we’ll tell you all about how we work according to the principles of APQP.
Quality Management System according to IATF 16949
Meldon has set up its Quality Management System according to IATF 16949. One of the requirements of an IATF 16949 is that we have a very effective quality management system. The high-quality standards indicated in the IATF 16949 mean we follow a very strict set of requirements for new product introduction (NPI) and mass production processes. Following these requirements is intended to prevent defects and process failures.
Advanced product quality planning
Effective risk management brings better control of quality and improved business success. Meldon utilizes the Advanced product quality planning (APQP) methodology. APQP will minimize the risks inherent to the production processes, such as process failures. For this reason, we use the APQP process for new product and process developments (NPI). APQP is part of the five Core Tools (IATF 16949-compliant) for effective quality management with PPAP, FMEA, MSA, and SPC being the other core tools.
APQP consists of four main phases:
- Planning phase
- Product design & Development support phase
- Process design & Development phase
- Product & Process Validation phase
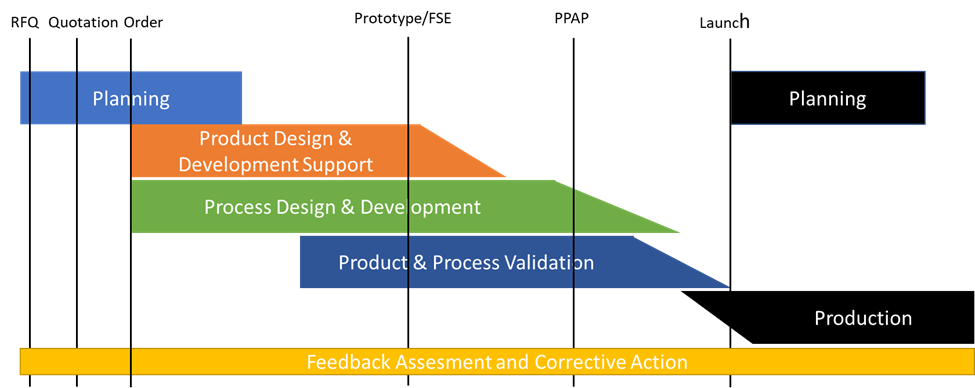
The development process of a new product usually starts with a quote request from our customer. Usually in the form of a technical concept drawing. The sales department processes the application and starts the development process according to the APQP methodology. APQP provides us with a structured process to ensure customer satisfaction with new products both in the development phase as in the production phase.
We would like to illustrate these four stages using our internal process for developing a new extrusion profile.
1. Planning phase: gather information
One of the most important pieces of information in the planning phase is the expected function of the extrusion parts and/or assembly. This information helps the engineering team to evaluate the request and the potential design constraints during a feasibility study. For simple products, the process is fairly straightforward. However, when the design is complex, we schedule a meeting with all parties involved. During this meeting, we discuss all the details, including:
- the application
- the purpose of the extrusion
- the tolerances involved
- the specified material
- the possible obstacles to be overcome
- the operating environment of the part
- any (specific) customer requirements
All this information together guides us during our evaluation and planning phase.
Following this exchange of information, we will begin the process of designing an extrusion that takes into consideration all the elements. One goal we have is to design a part that meets the application the customer has in mind. This involves an analysis of the required tolerances and fit. The second goal is to design an extrusion that is optimized for the extrusion process. This is important because the ultimate goal is to define an extrusion that is both cost-effective and consistently reliable.
Technical drawings and quotation
If needed we will then submit a technical drawing or propose changes to the customer supplied drawings. Thanks to our vast experience with extrusion, we know that certain profile shapes can provide challenges to the extrusion process. When designing the extrusion part, we naturally take into account as many circumstances as possible. However, it is important to inform us what the expected results are, to ensure we meet your expectations. As soon as an agreement is reached on the proposed design (changes), we will issue a written quotation.
2. Product design & Development support phase
After receiving a purchase order to continue with the development of the profile, we start the second phase of the APQP process: “Product design & Development support”. We will select suppliers and begin the process of designing the tooling and measurement elements necessary to manufacture the extrusion. The goal of this phase is to finish the product design, as well as the feasibility assessment.
3. Process design & Development
In phase 3 “Process design & Development” we plan the manufacturing process for the product. The goal is to consider product specifications, product quality, and production costs when designing and developing the production process. The process must be able to run smoothly and produce the expected quantities to keep up with consumer demands.
First evaluations and trials
In this stage a Process-FMEA is carried out by a multidisciplinary team. And a control plan is extracted from the p-FMEA. The tooling is made in our own tool shop. When all the elements are complete, the tooling will be assembled onto an extruder for the first trial to evaluate the flow of the plastic(s).
For complex profiles, each trial has its own goal with respect to what element of the shape we are trying to evaluate at that point. After each trial, modifications are made to the tools to get us closer to the completed part. The typical profile requires several trials before samples are ready for the customer’s evaluation.
First sample evaluation
When the shape is completed, so-called First Sample Evaluation (FSE) samples are sent to the customer for evaluation of the design. From there, we are ready to respond to the customer’s needs for additional samples or production. Once an extrusion is completed, the process is stable and the product meets the (customer)requirements, phase 4 can be started.
4. Product & Process validation
This is the test phase for validating the manufacturing process and the final product in a production environment with operators. The end results of this phase include confirmation to the capability and reliability of the manufacturing process, and the product quality acceptance criteria. Trial production runs (PPAP) are made, and product output is tested to confirm the effectiveness of the deployed manufacturing approach. Any needed adjustments are reconciled before moving on to production.
Production and improvement
The production occurs in this phase, with an emphasis on evaluating and improving processes. Activities such as reducing process variations, identifying issues, and starting corrective actions to support continual improvement are mainstays in this phase. Collecting and assessing customer feedback, as well as collecting data related to process efficiency and quality planning effectiveness, is important in this phase.
How may we help you?
Do not hesitate to contact us for more information or to make an enquiry.





